DHCP stands for Dynamic Host configuration protocol. It is used to dynamically assign IP addresses to the systems. We require IP addresses to access the internet for communication purposes. It acts as an identifier for a network device like you have a location so letters can be sent to you likewise a web page cannot be downloaded without an IP address, so to make the internet accessible IP address should be relegated to your device by the network administrator.
Two ways that a computer can assign an IP address are Static IP or Dynamic IP:
Static IP
In this, the user assigns an IP address manually. This was the original method that was done at the beginning of the networking. You have a computer network configuration page for each device and type the IP address manually. In addition to this, you also have to type a subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server. You do the same every time you incorporate a new device. It was not feasible with a lot number of devices. All the IP addresses should be unique to avoid the IP conflict.
Dynamic IP
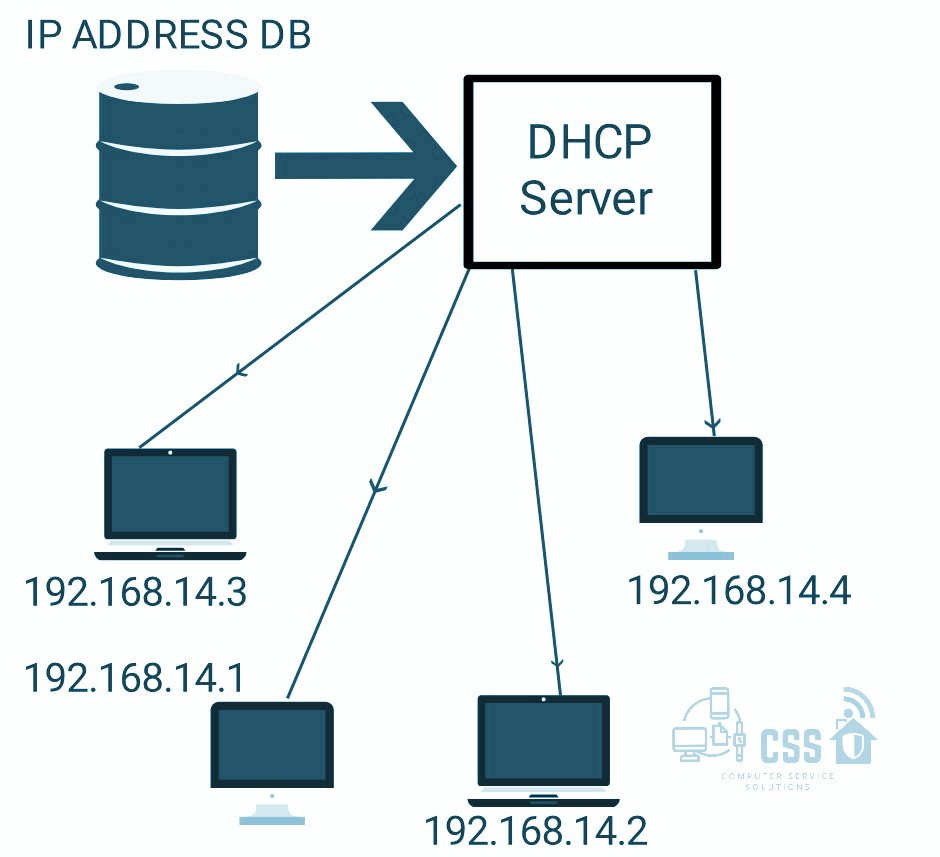
In this, the device automatically receives an IP address from a DHCP server. It also features a subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server. Our home router supports an embedded DHCP server. The process by which DHCP client obtains an IP address from the DHCP server is known as the DORA process.
DHCP architecture
It is made up of DHCP clients, DHCP servers, and DHCP relay agents.
- DHCP client –Any device which can connect to the network and can communicate with a DHCP server. It uses the options to transfer additional IP settings to DHCP clients including default gateway IP address and DNS domain name.
- DHCP servers – It is a device on a network with the list of IP addresses to allocate the new devices automatically.
- DHCP relay agent – They pass DHCP messages between the server and the client. Dealing with large and complex networks needs this.
How DHCP Protocol Works?
DHCP protocol operates on the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack to dynamically assign IP addresses & configuration information to DHCP clients. The DHCP server contains a range of IP addresses that it can give out. If the address is available it will send the response containing the subnet mask information, default gateway IP addresses, domain name system (DNS) addresses, and the lease time the computer can use the address for.
DHCP is based on the client-server architecture in which servers have to manage a pool of unique IP addresses, as well as information about client configuration parameters, and lease IP address out of the pool for a specific period. Once the lease is ready to expire, the client will contact the server to arrange renewal arrangements. The IP address is leased so that the range of IP addresses can be recycled and not used up or left as used by a device that has been disconnected. You may reserve the device’s address via DHCP.
DHCP clients obtain a DHCP lease for an IP address, a subnet mask, and various DHCP options from DHCP servers in a four-step process:

- DHCP discover – At this stage, the client has no IP address and no DHPC server address. Thus, the client broadcasts a DHCP server request.
- DHCP offer – The DHCP server receives the discover request. This enables the DHCP server to respond with an Offer for an IP address back to the client.
- DHCP request -The client broadcasts a request to lease an address from one of the offering DHCP servers.
- DHCP acknowledges -The DHCP server that the client responds to acknowledges the client, assigns it any configured DHCP options and updates its DHCP database. The client then initializes and binds its TCP/IP protocol stack and can begin network communication.
Advantages of DHCP
- Centralized management of IP addresses: DHCP IP configuration information can be stored in a single location. And hence helps the administrator to centrally manage all configuration information for the IP address.
- Flexibility and scalability: Using DHCP gives greater flexibility to the administrator, allowing the administrator to move easily change IP configuration when the infrastructure changes.
- Dynamic host configuration: DHCP automates the process of configuring the host and eliminates the need to configure each host manually.
- No conflicts: It prevents duplicate or invalid assignment of IP addresses. Hence there is no possibility of conflicting IP addresses.
Drawbacks of DHCP
- Security: Provided that the DHCP server does not have a protected client authentication mechanism, it can obtain unauthorized access to IP addresses by providing credentials such as client identifiers that belong to other DHCP clients.
- No access: Clients cannot access the network in the absence of the DHCP server.
Attacks & Security
DHCP Starvation attack
DHCP starvation attack aims to attack the DHCP server by using fake requests. It results in the consumption of all available IP Addresses. For the original users, it`s like a denial of service attack where user requests cannot be fulfilled.
Prevention: Implement same source MAC Address check on DHCP requests and DHCP Snooping.
DHCP Spoofing attack
Unlike in the DHCP starvation, In, DHCP spoofing, the attacker tries to send a forged response to DHCP request. The attacker acts like a DNS server or default gateway. This attack may lead to DoS. Also as the attacker spoofs the default gateway, user traffic interception is also possible.
Prevention: We use DHCP snooping technique to prevent DHCP spoofing. In this technique, the creation of anti-spoofing filters takes place. We basically configure the switch to detect the malicious packets in the DHCP traffic. The technique works on wired communication networks only.
With DHCP Snooping we can:
- Filter and validate messages
- Build, manage and maintain the binding database.
Click here to Learn everything about the SMTP Protocol.








